- 1. Organic/Agric Waste recycling:
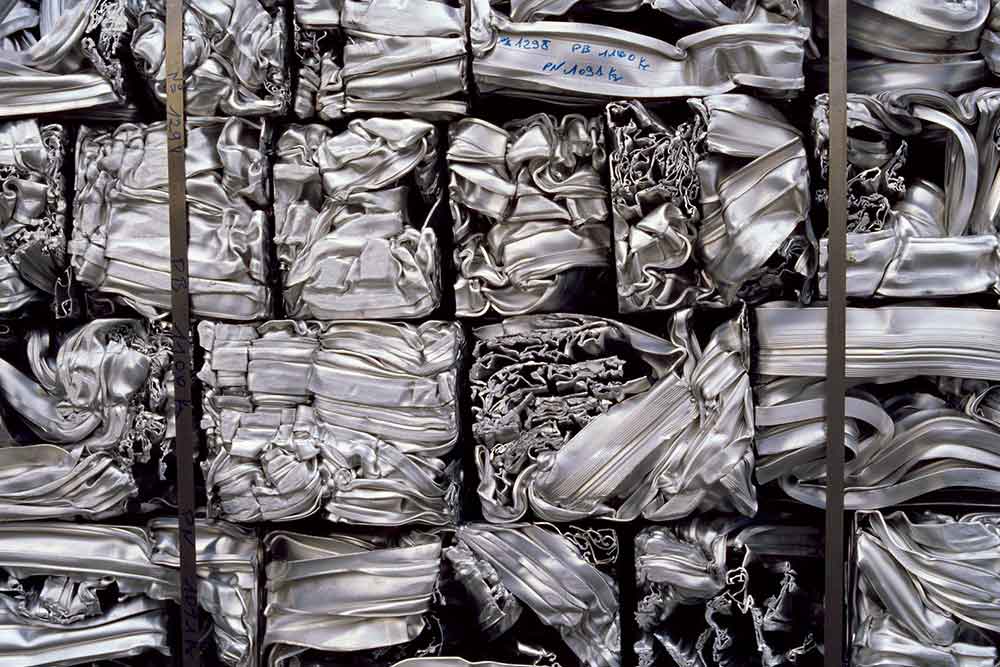
- 2. Aluminium waste recycling
- 3. Waste tyres recycling
- 4. Lead Acid battery collection and recycling:
- 5. Solar panel recycling
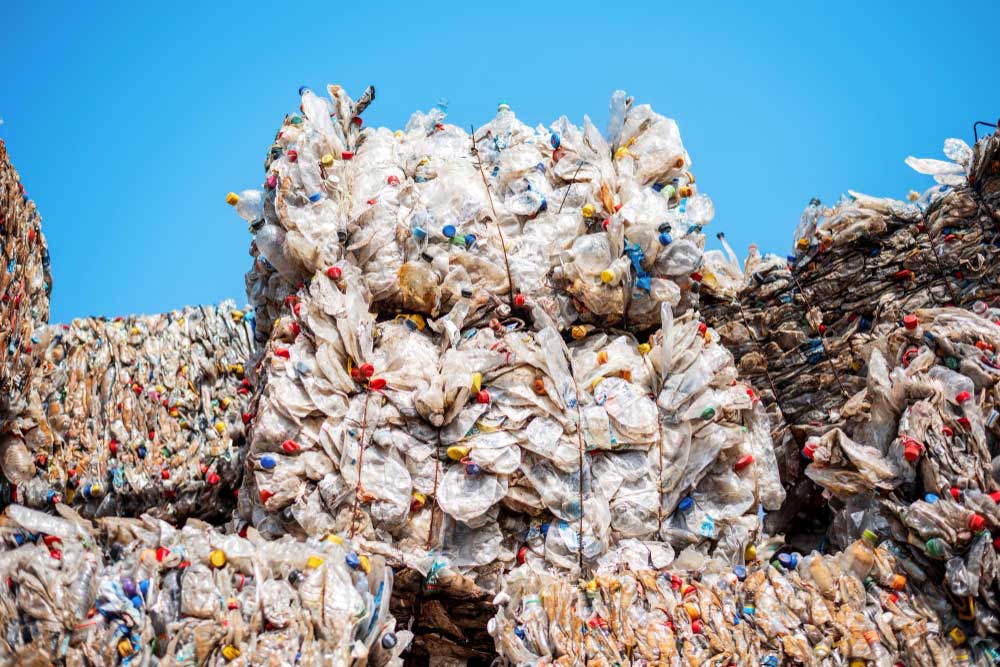
- 6. Plastic Waste recycling
Egg Shell Powder Manufacturing


Aluminium waste recycling

Waste tyres recycling
Rubber Mulch
Due to its lack of soil nutrients, rubber mulch can also act as a barrier between soil and sunlight, meaning that deters weeds and insects. It is also a much more durable option than using wood chippings.


Recycled tires playground
Recycled tires for asphalt

Rubberized bricks, interlocks and tiles
Shoe sole production
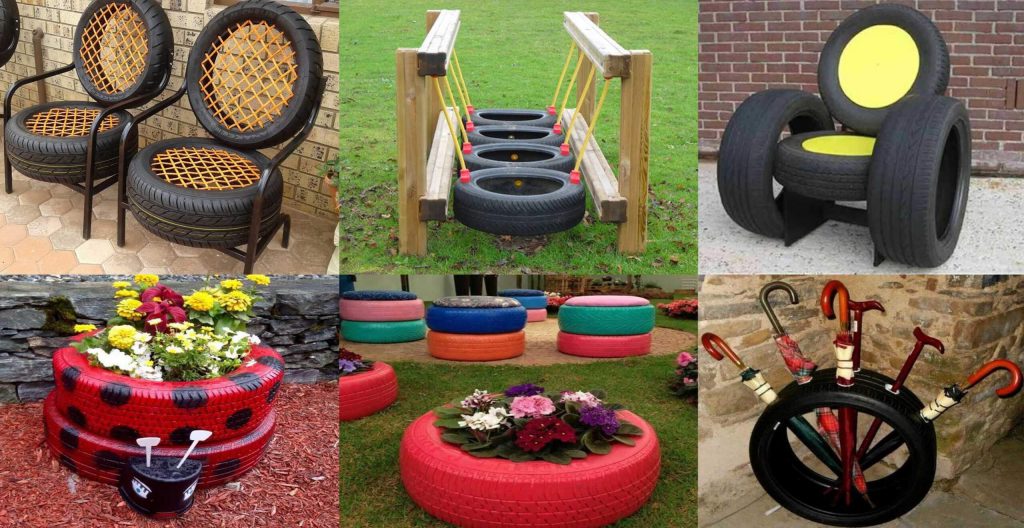


Turning Waste Tyres into Furniture:
Converting waste Tyres into Furniture and Work of Art is an innovative and sustainable solution to address environmental challenges. Repurposing discarded tyres into functional items like Furniture and Bricks reduces waste and conserves resources. This approach is highly impactful in addressing two critical issues simultaneously: environmental degradation and resource depletion.
Therefore, we must encourage and promote this sustainable solution to create a more sustainable future. The
repurposing of old tyres into outdoor furniture and bricks is a highly effective and sustainable solution. Tyre rubber’s durable and resilient nature makes it ideal for creating furniture that can withstand harsh weather conditions. Additionally, converting tyre waste into bricks is an effective way to reduce environmental pollution and promote sustainable construction practices.
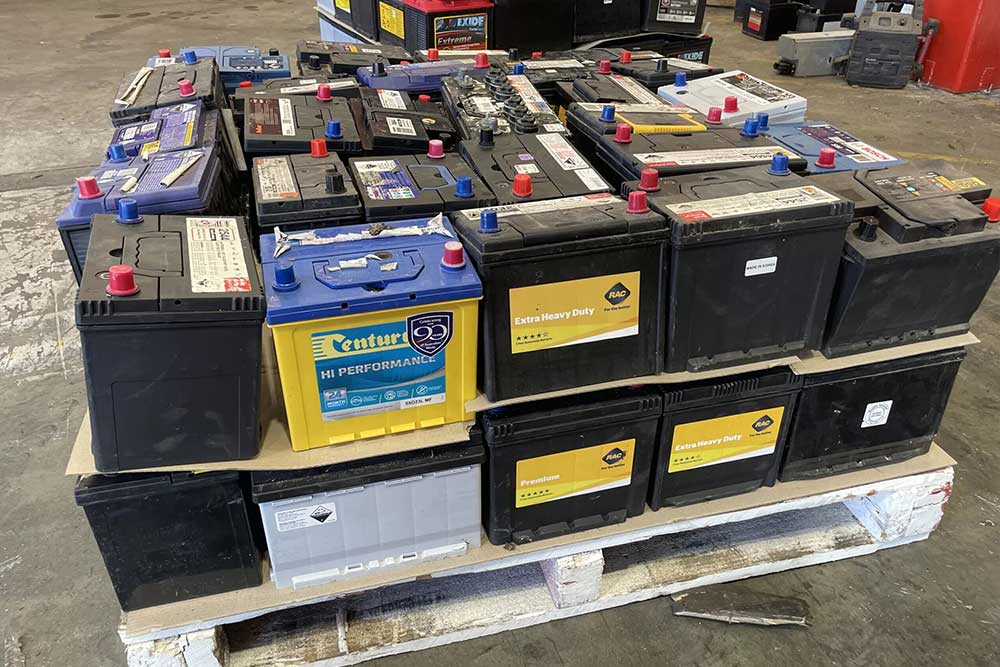
Lead Acid battery collection and recycling:
Lead-acid battery recycling offers substantial economic value through the recovery and reuse of valuable materials. Lead, in particular, is a highly sought-after commodity in various industries, including automotive, construction, and manufacturing. By recycling lead-acid batteries, manufacturers can obtain a reliable and cost-effective source of lead, reducing their dependence on primary lead production and mitigating price volatility in the lead market. Additionally, recycling reduces the need for virgin materials, lowering production costs and enhancing supply chain resilience. It also helps local economies by creating jobs and expanding employment. Recycling facilities require a skilled workforce to operate machinery, perform quality control checks, and manage logistics.
Furthermore, the expansion of recycling infrastructure and the implementation of recycling initiatives create demand for ancillary services such as transportation, warehousing, and engineering consultancy, further bolstering economic activity and the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). In addition to direct economic benefits, this recycling contributes to resource conservation and cost savings across industries. By recycling lead-acid batteries, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on virgin materials, conserving natural resources and minimizing environmental degradation associated with mining and extraction.
Moreover, recycling helps companies avoid the costs of waste disposal and environmental clean-up, including regulatory compliance, landfill fees, and liability for pollution-related damages. By incorporating recycled materials into their production processes, companies can achieve cost savings while enhancing their sustainability credentials.


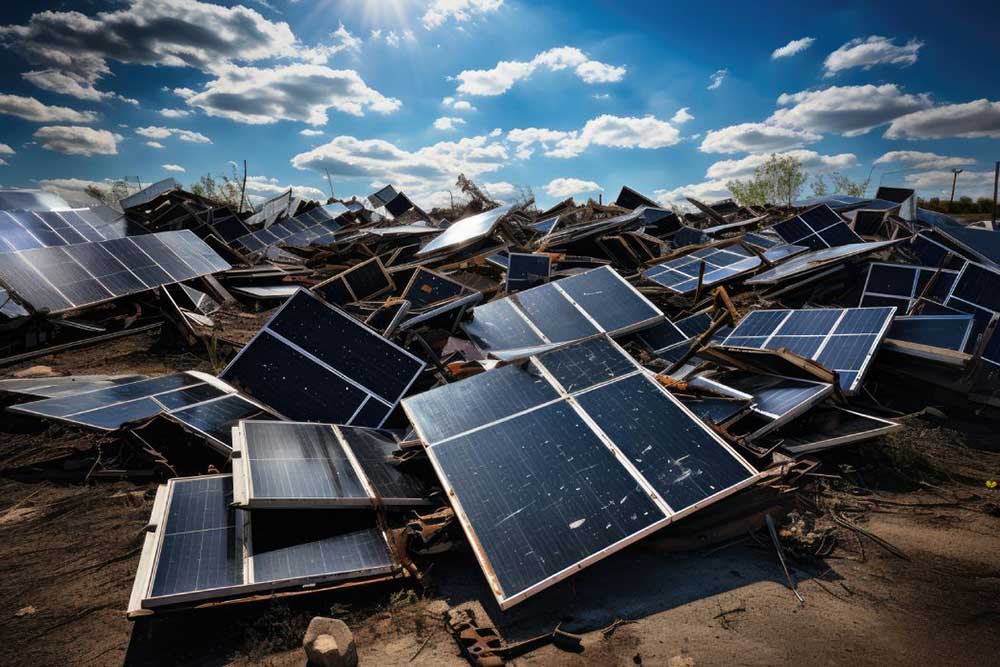
Solar panel recycling
Solar panels are composed of a variety of materials, including silicon, glass, aluminum, copper, and more. These materials are not readily replenished in nature, and their extraction often involves mining processes that can lead to environmental degradation. By recycling solar panels, we can recover up to 95% of these materials, minimizing the need for resource extraction and the associated environmental impacts.
The solar panel industry is rapidly expanding, and with it comes the potential for a growing market for recycled solar materials. Recycling these materials creates jobs and opportunities for businesses focused on resource recovery and processing. This contributes to a thriving circular economy that promotes sustainable practices and economic growth. Moreover, recycling solar panels helps to reduce the cost of producing new panels, making solar energy more affordable and accessible to a wider range of consumers. This, in turn, accelerates the transition to renewable energy sources and reduces our reliance on fossil fuels. As we move towards a future powered by renewable energy, solar panel recycling will play an increasingly important role. By prioritizing resource recovery and circular practices, we can ensure that solar energy remains a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for generations to come. Solar panel recycling is not just about environmental protection; it’s also about ensuring the long-term sustainability of the solar industry and creating a circular economy for solar panels. By minimizing waste, reducing costs, and making solar energy a more attractive and viable option to power our homes, businesses, and communities


Plastic Waste recycling
One of the primary economic benefits of plastic recycling is the cost reduction in acquiring raw materials. Producing plastic from virgin materials is often more expensive than using recycled plastic. By recycling plastic, manufacturers can lower their production costs, leading to increased profitability and competitiveness. Plastic recycling offers numerous economic benefits that go beyond environmental sustainability. It helps reduce the acquisition costs of raw materials, saves energy, creates job opportunities, and minimises waste management expenses. Embracing plastic recycling is a win-win situation for both businesses and society, leading to a more prosperous and sustainable future.
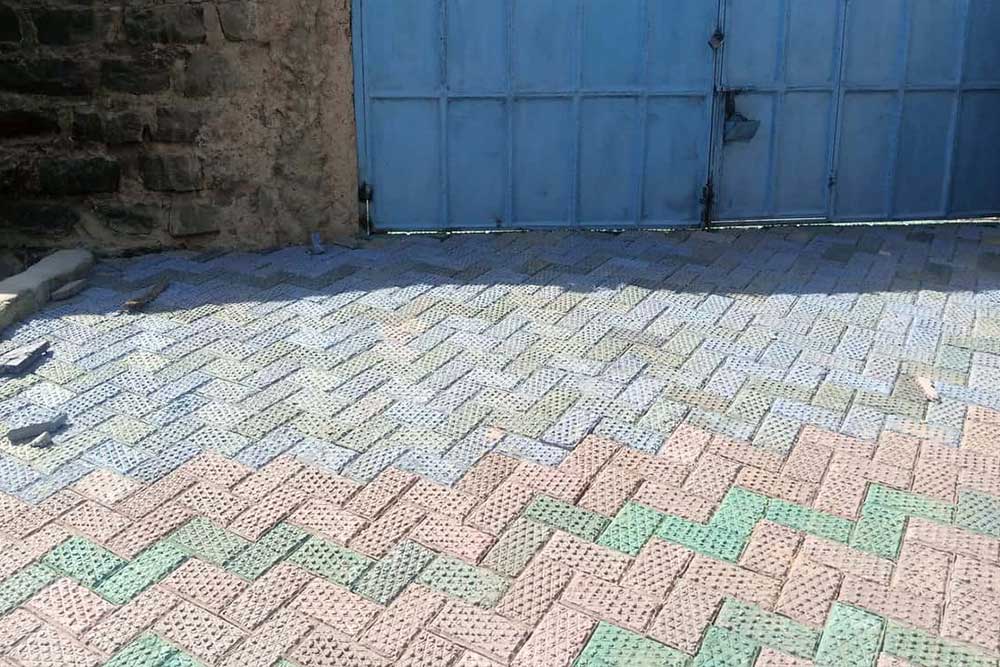
Conversion of LDPE Waste Plastics to Interlocks (Paving Stones):
As the demand for construction materials increases, finding alternative, readily available, and cost-effective options is becoming imperative. The disposal of plastic waste in the environment poses a significant problem due to its low biodegradability and the vast quantities in which it exists. Homes flooded with water due to blocked gutters filled with plastic waste and streets cluttered with single-use plastics are constant, graphic reminders of this issue.
This project explores the recycling of waste plastic, specifically Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), as a complete replacement for Portland cement in the production of interlocking paving stones. Recycling plastic waste to produce these interlocks would greatly benefit the construction industry by significantly reducing costs and promoting a healthier, more sustainable environment.


